What’s Tetany? Understanding the Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Have you ever experienced muscle cramps or spasms that seem to come out of nowhere? It could be tetany, a condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions and spasms. Understanding what’s tetany, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for anyone experiencing these uncomfortable and sometimes debilitating episodes. This article will delve into the details of what’s tetany, providing a comprehensive overview to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Defining Tetany: More Than Just Muscle Cramps
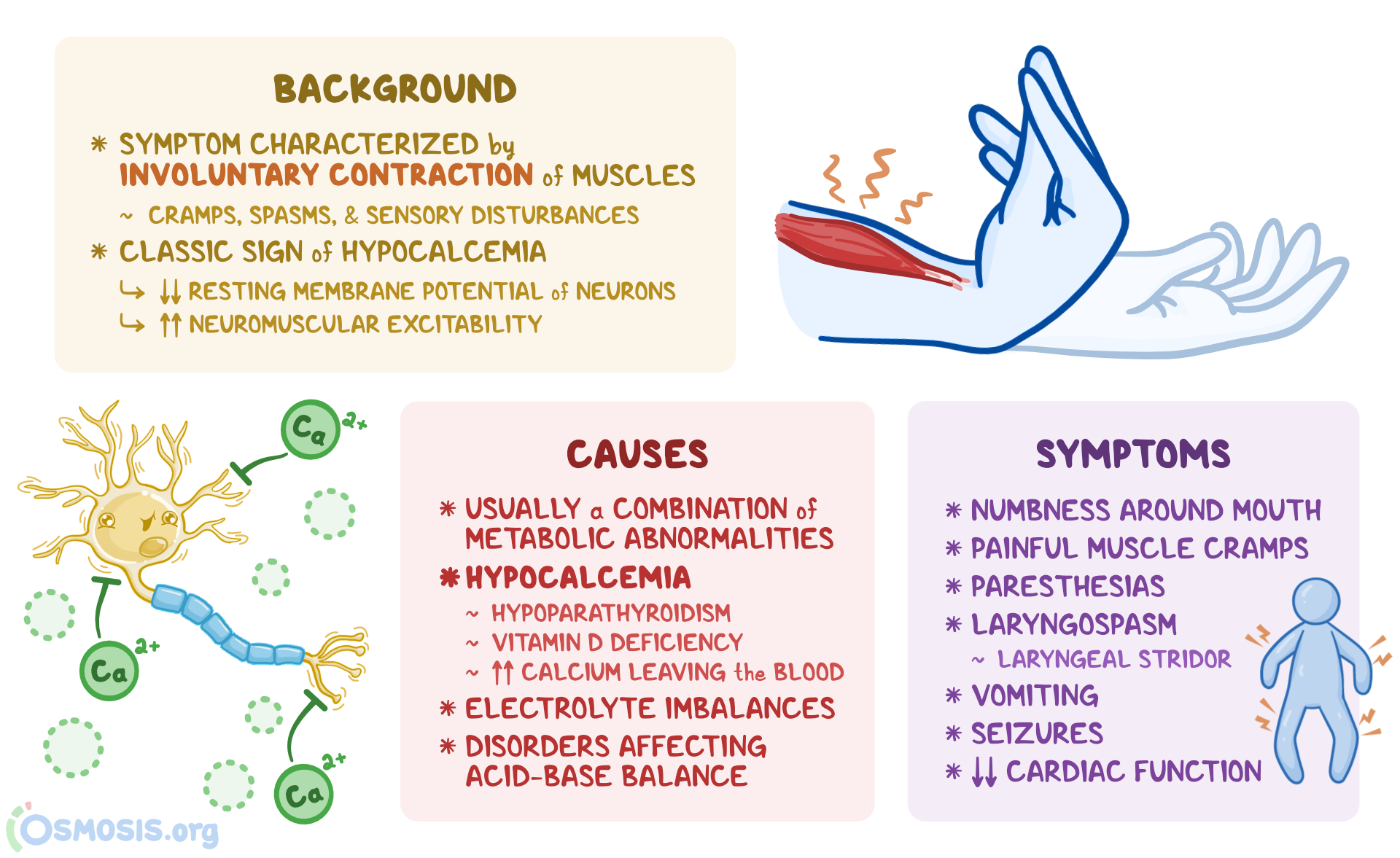
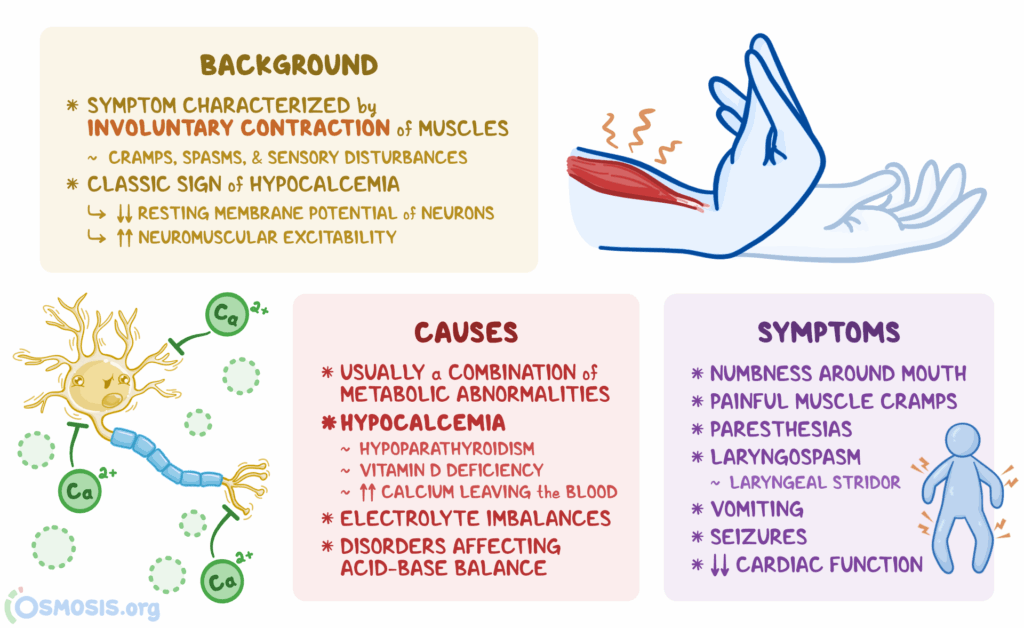
What’s tetany, exactly? Tetany isn’t a disease in itself, but rather a symptom of an underlying problem. It manifests as muscle spasms, cramps, and tremors, often affecting the hands, feet, and face. These involuntary contractions can range from mild twitches to severe and painful spasms that can last for several minutes. The intensity and frequency of tetanic episodes can vary significantly from person to person.
Distinguishing tetany from regular muscle cramps is important. While cramps might be caused by dehydration or overexertion, tetany usually stems from electrolyte imbalances, particularly low levels of calcium, magnesium, or potassium in the blood. Therefore, understanding what’s tetany involves recognizing its underlying physiological causes.
The Root Causes: Why Does Tetany Occur?
Several factors can contribute to the development of tetany. The most common cause is hypocalcemia, or low blood calcium levels. Calcium plays a vital role in nerve and muscle function, and when levels drop too low, it can lead to increased excitability of nerves, triggering muscle spasms. Other common causes include:
- Hypomagnesemia (Low Magnesium): Magnesium is essential for calcium regulation and nerve function. A deficiency can disrupt calcium balance and contribute to tetany.
- Hypokalemia (Low Potassium): Potassium is crucial for maintaining proper nerve and muscle cell function. Low potassium levels can alter the electrical activity of cells, leading to tetany.
- Alkalosis: An increase in blood pH (alkalosis) can decrease the amount of ionized (active) calcium in the blood, even if the total calcium level appears normal. This can cause tetany.
- Hyperventilation: Rapid and deep breathing can lead to alkalosis, further exacerbating calcium imbalances.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, can increase the excretion of calcium and magnesium, potentially leading to tetany.
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can affect electrolyte balance and vitamin D metabolism, contributing to hypocalcemia and tetany.
- Parathyroid Disorders: The parathyroid glands regulate calcium levels in the blood. Disorders affecting these glands can lead to hypocalcemia and tetany.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption from the gut. Deficiency can lead to low calcium levels and tetany.
Knowing what’s tetany also means understanding that identifying the underlying cause is critical for effective treatment. If you suspect you have tetany, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Recognizing the Symptoms: What Does Tetany Feel Like?
The symptoms of tetany can vary depending on the severity of the electrolyte imbalance and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle Spasms and Cramps: These are the hallmark symptoms of tetany, often affecting the hands, feet, arms, and legs. The spasms can be painful and debilitating.
- Tingling and Numbness: A tingling or numbness sensation, particularly around the mouth, fingers, and toes, is a common early symptom.
- Muscle Twitching (Fasciculations): Small, involuntary muscle twitches can occur, particularly in the eyelids or facial muscles.
- Carpopedal Spasm: This involves involuntary contraction of the muscles in the hands and feet, causing the fingers to flex and the toes to point downwards.
- Laryngospasm: In severe cases, the muscles of the larynx (voice box) can spasm, leading to difficulty breathing and a sensation of choking. This is a medical emergency.
- Seizures: In extreme cases of severe hypocalcemia, seizures can occur.
Understanding what’s tetany involves recognizing these symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention if you experience them, especially if accompanied by difficulty breathing or seizures.
Diagnosing Tetany: Finding the Root Cause
Diagnosing tetany involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you are taking. A physical examination may include assessing your muscle strength and reflexes. The following laboratory tests are commonly used to diagnose tetany:
- Blood Calcium Level: Measures the amount of calcium in your blood. Low calcium levels are a key indicator of tetany.
- Blood Magnesium Level: Measures the amount of magnesium in your blood.
- Blood Potassium Level: Measures the amount of potassium in your blood.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG): Measures the pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels in your blood. This can help identify alkalosis.
- Kidney Function Tests: Assess kidney function, as kidney disease can contribute to electrolyte imbalances.
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Level: Measures the level of parathyroid hormone in your blood. This can help identify parathyroid disorders.
- Vitamin D Level: Measures the level of vitamin D in your blood.
Once the underlying cause of tetany is identified, appropriate treatment can be initiated. Knowing what’s tetany from a diagnostic perspective allows for targeted therapeutic interventions.
Treating Tetany: Restoring Electrolyte Balance
The treatment for tetany focuses on correcting the underlying electrolyte imbalance and alleviating the symptoms. The specific treatment will depend on the cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Calcium Supplementation: For hypocalcemia, calcium can be administered intravenously (IV) in severe cases or orally for milder cases.
- Magnesium Supplementation: For hypomagnesemia, magnesium can be administered IV or orally.
- Potassium Supplementation: For hypokalemia, potassium can be administered IV or orally.
- Addressing Alkalosis: Treatment for alkalosis may involve breathing into a paper bag to increase carbon dioxide levels in the blood, or administering medications to lower blood pH.
- Treating Underlying Conditions: If tetany is caused by kidney disease, parathyroid disorders, or vitamin D deficiency, treatment will focus on addressing these underlying conditions.
In addition to addressing the underlying cause, medications such as muscle relaxants may be used to alleviate muscle spasms and cramps. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation. Understanding what’s tetany also means understanding that treatment is individualized based on the underlying etiology.
Preventing Tetany: Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
While not all cases of tetany are preventable, certain lifestyle and dietary modifications can help reduce the risk. These include:
- Maintaining a Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Good sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods. Magnesium is found in nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables. Potassium is abundant in bananas, potatoes, tomatoes, and spinach.
- Vitamin D Supplementation: If you are deficient in vitamin D, consider taking a supplement to improve calcium absorption.
- Staying Hydrated: Dehydration can exacerbate electrolyte imbalances. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Managing Stress: Stress can contribute to hyperventilation, which can lead to alkalosis and tetany. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoiding Excessive Alcohol and Caffeine: These substances can interfere with electrolyte balance.
- Consulting with Your Doctor: If you have a medical condition that increases your risk of tetany, such as kidney disease or parathyroid disorders, work closely with your doctor to manage your condition and prevent electrolyte imbalances.
By understanding what’s tetany and making these lifestyle changes, you can proactively reduce your risk of developing this uncomfortable condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of tetany, especially if they are severe or persistent. Seek immediate medical care if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing
- Seizures
- Severe muscle spasms that interfere with your ability to function
- Loss of consciousness
These symptoms could indicate a life-threatening electrolyte imbalance that requires immediate treatment. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications. Knowing what’s tetany empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
What’s tetany? It’s a condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions and spasms, often caused by electrolyte imbalances. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies discussed in this article, you can take control of your health and manage this condition effectively. If you suspect you have tetany, consult with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment. Early diagnosis and management can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Remember, being informed about what’s tetany is the first step towards better health.
[See also: Hypocalcemia Symptoms and Treatment]
[See also: Magnesium Deficiency: Signs and Solutions]
[See also: Understanding Electrolyte Imbalance]