Tetany in Hands: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Experiencing muscle spasms or cramps in your hands can be unsettling. When these spasms become frequent and intense, it could be a sign of tetany, specifically tetany in hands. Tetany is a condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions and cramps, often resulting from electrolyte imbalances, particularly low calcium levels. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for tetany in hands, providing a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
What is Tetany?
Tetany is a neuromuscular condition characterized by muscle spasms, cramps, and twitching. These symptoms are often caused by disruptions in the body’s electrolyte balance, primarily involving calcium, magnesium, and potassium. While tetany can affect various parts of the body, its manifestation in the hands is a common and often distressing experience.
Causes of Tetany in Hands
Several factors can contribute to the development of tetany in hands. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. The most common causes include:
Hypocalcemia (Low Calcium Levels)
Hypocalcemia, or low calcium levels in the blood, is the leading cause of tetany. Calcium plays a vital role in nerve and muscle function. When calcium levels drop, nerves become more excitable, leading to involuntary muscle contractions. Conditions that can lead to hypocalcemia include:
- Hypoparathyroidism: Underactive parathyroid glands produce insufficient parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium levels.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption from the gut. A deficiency can lead to reduced calcium levels.
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can disrupt calcium regulation.
- Malabsorption: Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease can interfere with calcium absorption.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, can increase calcium excretion.
Hypomagnesemia (Low Magnesium Levels)
Magnesium is another essential electrolyte involved in nerve and muscle function. Low magnesium levels can exacerbate the effects of hypocalcemia and contribute to tetany in hands. Causes of hypomagnesemia include:
- Malnutrition: Inadequate dietary intake of magnesium.
- Alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair magnesium absorption.
- Diarrhea and Vomiting: Prolonged diarrhea or vomiting can lead to magnesium loss.
- Certain Medications: Diuretics and some antibiotics can increase magnesium excretion.
Hyperventilation
Rapid and deep breathing, or hyperventilation, can lead to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels in the blood, causing respiratory alkalosis. This alkalosis can reduce the amount of ionized calcium, the form of calcium that is biologically active, leading to tetany in hands.
Alkalosis
Any condition that increases the pH of the blood (making it more alkaline) can decrease the amount of ionized calcium, potentially triggering tetany. This can be caused by hyperventilation, as mentioned, or other medical conditions.
Symptoms of Tetany in Hands
The symptoms of tetany in hands can vary in severity, but common manifestations include:
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions of the hand muscles.
- Cramps: Painful muscle contractions that can last for several minutes.
- Tingling and Numbness: Paresthesia, or abnormal sensations, in the fingers and hands.
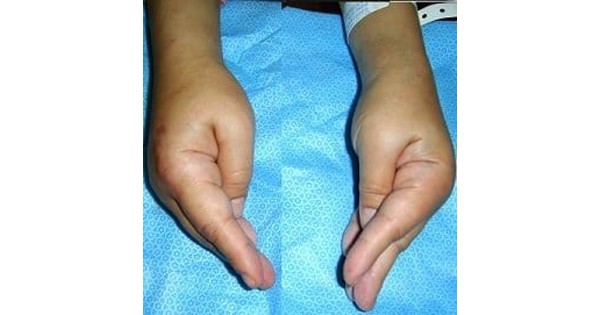
- Carpopedal Spasm: A characteristic posture where the wrist and fingers are flexed, and the thumb is adducted (Trousseau’s sign). This can often be elicited by inflating a blood pressure cuff on the arm.
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty with fine motor movements and grip strength.
In severe cases, tetany can also affect other muscles in the body, leading to generalized muscle spasms, seizures, and even respiratory distress. Prompt medical attention is crucial if these symptoms occur.
Diagnosis of Tetany in Hands
Diagnosing tetany in hands involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The diagnostic process typically includes:
Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, medications, and dietary habits. A physical examination will assess muscle strength, reflexes, and signs of carpopedal spasm (Trousseau’s sign) or facial muscle twitching (Chvostek’s sign, elicited by tapping on the facial nerve).
Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for measuring electrolyte levels, including calcium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphate. These tests can help identify the underlying cause of tetany. Additional blood tests may be ordered to assess kidney function, parathyroid hormone levels, and vitamin D levels.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG may be performed to assess heart function, as electrolyte imbalances can affect the heart’s electrical activity.
Electromyography (EMG)
In some cases, an EMG may be used to evaluate the electrical activity of muscles and nerves, helping to differentiate tetany from other neuromuscular disorders.
Treatment of Tetany in Hands
The treatment for tetany in hands focuses on correcting the underlying electrolyte imbalances and alleviating symptoms. Treatment options may include:
Calcium Supplementation
For hypocalcemia-induced tetany, calcium supplementation is the primary treatment. This can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the condition. Oral calcium supplements, such as calcium carbonate or calcium citrate, are typically used for mild to moderate hypocalcemia. Intravenous calcium gluconate is reserved for severe cases or when oral supplementation is not feasible.
Magnesium Supplementation
If hypomagnesemia is contributing to tetany, magnesium supplementation is necessary. Oral magnesium supplements, such as magnesium oxide or magnesium citrate, can be used for mild to moderate deficiency. Intravenous magnesium sulfate is used for severe cases or when oral supplementation is not tolerated.
Vitamin D Supplementation
If vitamin D deficiency is identified, supplementation with vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) or vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is recommended to improve calcium absorption.
Treatment of Underlying Conditions
Addressing the underlying cause of electrolyte imbalances is crucial for long-term management of tetany. This may involve treating hypoparathyroidism, kidney disease, malabsorption disorders, or other medical conditions. [See also: Understanding Parathyroid Disorders]
Symptomatic Relief
In addition to correcting electrolyte imbalances, symptomatic relief measures can help alleviate muscle spasms and cramps. These may include:
- Muscle Relaxants: Medications like benzodiazepines can help reduce muscle spasms.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help relax muscles and reduce pain.
- Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises can help relieve muscle cramps and improve flexibility.
Prevention of Tetany in Hands
Preventing tetany in hands involves maintaining adequate electrolyte levels and addressing underlying medical conditions. Preventive measures include:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D.
- Supplementation: Taking calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D supplements as recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to promote bone health and muscle strength.
- Avoiding Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake to prevent magnesium deficiency.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Effectively managing medical conditions like hypoparathyroidism, kidney disease, and malabsorption disorders.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience frequent or severe muscle spasms, cramps, or tingling in your hands, it is important to seek medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe muscle spasms or cramps
- Difficulty breathing
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
Living with Tetany in Hands
Living with tetany in hands can be challenging, but with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life. Key strategies for managing tetany include:
- Adhering to Treatment Plans: Following your doctor’s recommendations for medication and supplementation.
- Monitoring Electrolyte Levels: Regularly monitoring your electrolyte levels through blood tests.
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups or online communities to connect with others who have similar experiences.
Conclusion
Tetany in hands is a condition characterized by muscle spasms, cramps, and tingling sensations, often caused by electrolyte imbalances, particularly low calcium or magnesium levels. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention. By maintaining adequate electrolyte levels, addressing underlying medical conditions, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals with tetany in hands can improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of this condition. If you suspect you have tetany, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. [See also: Calcium Deficiency and Its Effects]
