Securing Your Digital Assets: Understanding Cloud App Security
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly relying on cloud-based applications to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and drive innovation. From Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to productivity suites and file-sharing platforms, cloud apps have become indispensable tools for modern organizations. However, this widespread adoption also introduces new security challenges. Cloud app security is no longer an option; it’s a necessity.
This article delves into the crucial aspects of cloud app security, exploring the risks associated with cloud applications, the key components of a robust security strategy, and the best practices for protecting your organization’s data and infrastructure in the cloud. We’ll also examine the tools and technologies available to help you effectively manage and mitigate these risks, ensuring a secure and compliant cloud environment.
The Growing Need for Cloud App Security
The shift to the cloud has fundamentally changed the way organizations manage their data and applications. While cloud providers offer a shared responsibility model for security, businesses are ultimately responsible for securing their own data and access to cloud resources. Several factors contribute to the growing need for robust cloud app security:
- Increased Attack Surface: Cloud applications expand the attack surface, providing malicious actors with more opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access.
- Data Breaches and Compliance: A data breach in a cloud application can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties for non-compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Shadow IT: The proliferation of unsanctioned cloud applications, known as shadow IT, poses a significant security risk. These applications often lack adequate security controls and visibility, making them vulnerable to attacks.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent employees can intentionally or unintentionally compromise cloud app security, leading to data leakage or unauthorized access.
- Complex Cloud Environments: Managing security across multiple cloud platforms and applications can be complex and challenging, requiring specialized expertise and tools.
Key Components of a Cloud App Security Strategy
A comprehensive cloud app security strategy should encompass several key components to effectively protect your organization’s data and applications in the cloud:
Visibility and Discovery
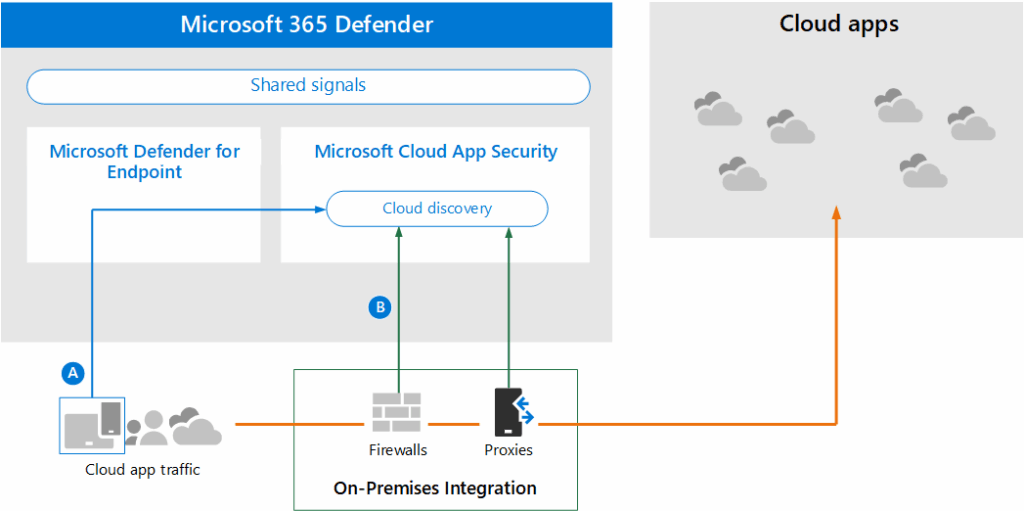
The first step in securing your cloud environment is gaining complete visibility into all cloud applications in use within your organization. This includes identifying both sanctioned and unsanctioned (shadow IT) applications. Tools like Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) can help discover and catalog all cloud apps, providing insights into their usage patterns and security risks.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP solutions are essential for preventing sensitive data from leaving your organization’s control. They can identify and protect sensitive data stored in cloud applications, such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, and intellectual property. DLP policies can be configured to block unauthorized data transfers, encrypt sensitive data, or alert administrators to potential data breaches.
Access Control and Identity Management
Implementing robust access control and identity management policies is crucial for securing cloud applications. This includes enforcing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC). Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions can help centralize user authentication and authorization, ensuring that only authorized users have access to specific cloud resources.
Threat Detection and Prevention
Proactive threat detection and prevention are essential for identifying and mitigating security threats in real-time. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can collect and analyze security logs from cloud applications, providing insights into potential security incidents. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) can detect and block malicious traffic and activity, preventing attacks from reaching your cloud applications.
Security Auditing and Compliance
Regular security audits and compliance assessments are necessary to ensure that your cloud app security measures are effective and aligned with industry best practices and regulatory requirements. These audits should cover all aspects of your cloud environment, including data security, access control, and incident response. Compliance frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS provide a standardized approach to security auditing and compliance.
Best Practices for Cloud App Security
Implementing a robust cloud app security strategy requires a combination of technology, policies, and processes. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Implement a Cloud Security Policy: Develop a comprehensive cloud security policy that outlines your organization’s security requirements for cloud applications. This policy should cover topics such as data security, access control, incident response, and compliance.
- Choose Secure Cloud Applications: When selecting cloud applications, prioritize those with strong security features and a proven track record of security. Look for applications that offer encryption, multi-factor authentication, and robust access control.
- Regularly Monitor Cloud App Usage: Continuously monitor cloud app usage to identify potential security risks and unauthorized activity. Use CASBs and other security tools to track app usage, detect anomalies, and enforce security policies.
- Educate Employees About Cloud Security: Train employees on cloud security best practices, including how to identify phishing attacks, protect their passwords, and avoid downloading malicious software.
- Regularly Update and Patch Cloud Applications: Ensure that all cloud applications are regularly updated and patched to address known vulnerabilities. Work with your cloud providers to ensure that security updates are applied promptly.
- Implement a Strong Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security incident in the cloud. This plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, and recovering from security breaches.
Tools and Technologies for Cloud App Security
Several tools and technologies can help organizations improve their cloud app security posture. Some of the most common include:
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): CASBs provide visibility into cloud app usage, enforce security policies, and detect threats. They act as intermediaries between users and cloud applications, providing a central point of control for security.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: DLP solutions prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization’s control. They can identify and protect sensitive data stored in cloud applications, such as PII, financial data, and intellectual property.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from cloud applications, providing insights into potential security incidents. They can help identify and respond to threats in real-time.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solutions: IAM solutions centralize user authentication and authorization, ensuring that only authorized users have access to specific cloud resources. They can enforce strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions: EDR solutions monitor endpoints for malicious activity and provide threat detection and response capabilities. They can help protect against malware, ransomware, and other threats that target cloud applications.
The Future of Cloud App Security
As cloud adoption continues to grow, cloud app security will become even more critical. Emerging trends in cloud computing, such as serverless computing, containerization, and artificial intelligence (AI), will introduce new security challenges. Organizations will need to adapt their security strategies to address these challenges and ensure that their data and applications remain secure in the cloud.
One key trend is the increasing use of AI and machine learning (ML) to automate security tasks and improve threat detection. AI-powered security solutions can analyze vast amounts of data to identify anomalies and predict potential security incidents. They can also automate incident response, reducing the time it takes to contain and recover from security breaches.
Another important trend is the growing focus on zero-trust security. Zero-trust security assumes that no user or device is trusted by default, and requires strict verification before granting access to cloud resources. This approach can help prevent unauthorized access and limit the impact of security breaches.
Conclusion
Cloud app security is a critical aspect of modern cybersecurity. As organizations increasingly rely on cloud applications, it’s essential to implement a robust security strategy to protect data and infrastructure. By understanding the risks associated with cloud applications, implementing key security components, and following best practices, businesses can ensure a secure and compliant cloud environment. Investing in the right tools and technologies is also crucial for effectively managing and mitigating these risks. In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, prioritizing cloud app security is not just a best practice; it’s a business imperative. [See also: Cloud Security Best Practices] [See also: Data Loss Prevention Strategies]

