Navigating the Autism Controversy: Understanding the Debates and Discussions
The landscape surrounding autism is complex, often punctuated by scientific advancements, evolving diagnostic criteria, and deeply personal narratives. However, this complexity also gives rise to the autism controversy, a collection of debates and discussions encompassing the etiology, treatment, and societal perception of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Understanding these controversies is crucial for fostering informed conversations, promoting ethical practices, and ultimately, supporting individuals with autism and their families. This article aims to explore the key areas of contention within the autism controversy, providing a balanced and fact-checked overview of the ongoing discussions.
The Etiology Debate: Genes, Environment, and the Search for Causes
One of the central aspects of the autism controversy revolves around its causes. While there is a broad consensus that autism is primarily a neurodevelopmental condition with a strong genetic component, the precise interplay between genes and environmental factors remains a subject of intense research and debate.
Genetic Predisposition: A Complex Puzzle
Numerous studies have identified hundreds of genes associated with an increased risk of autism. However, no single gene is responsible for all cases of autism. Instead, it is believed that a combination of multiple genetic variations, each with a small effect, can contribute to the development of ASD. This polygenic model makes identifying specific causal genes challenging. Furthermore, the same genetic variations may manifest differently in different individuals, leading to the wide spectrum of symptoms observed in autism. This inherent complexity fuels the ongoing debate about the relative contribution of genetics to the autism controversy.
Environmental Factors: Exploring Potential Triggers
While genetics play a significant role, environmental factors are also believed to contribute to the risk of autism. These factors can include exposures during pregnancy, such as maternal infections, certain medications, and advanced parental age. Research into environmental risk factors is ongoing, but it’s crucial to emphasize that correlation does not equal causation. Many studies are observational, meaning they can identify associations but cannot definitively prove that a specific environmental factor directly causes autism. Responsible reporting and cautious interpretation are essential to avoid misleading or alarming the public, contributing further to the autism controversy. [See also: Understanding Autism Genetics]
The Vaccine Myth: A Debunked Controversy
Perhaps the most damaging and persistent aspect of the autism controversy is the debunked claim that vaccines cause autism. This claim originated from a fraudulent 1998 study published in The Lancet, which has since been retracted. Numerous subsequent studies, involving millions of children worldwide, have found no evidence of a link between vaccines and autism. Major health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), have unequivocally refuted the vaccine-autism link. Despite the overwhelming scientific evidence, the myth persists, fueled by misinformation and mistrust. This perpetuation of the vaccine myth poses a significant public health risk, as it can lead to decreased vaccination rates and increased susceptibility to preventable diseases.
Combating this misinformation requires clear and consistent communication from healthcare professionals, scientists, and public health officials. It also necessitates critical thinking and media literacy skills among the general public to discern credible sources of information from unreliable ones. Addressing the emotional drivers behind vaccine hesitancy, such as parental anxiety and concerns about child safety, is also crucial. [See also: Debunking the Vaccine-Autism Myth]
Treatment Approaches: Evidence-Based Practices vs. Unproven Therapies
Another area of the autism controversy concerns the best treatment approaches for individuals with autism. While evidence-based therapies, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), have demonstrated effectiveness in improving communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors, other unproven or potentially harmful therapies continue to be promoted.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): A Cornerstone Therapy
ABA is a scientifically validated therapy that uses principles of learning to teach new skills and reduce challenging behaviors. It involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps and providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors. ABA is often tailored to the individual needs of each person with autism and can be implemented in various settings, including homes, schools, and therapy centers. While ABA has been shown to be effective, it has also faced criticism, particularly regarding its intensity and potential for overuse. Ethical considerations and the importance of individualized treatment plans are crucial aspects of responsible ABA practice.
Unproven and Potentially Harmful Therapies: Proceed with Caution
A wide range of unproven therapies for autism exists, including chelation therapy, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and dietary interventions. These therapies lack scientific evidence of effectiveness and may even pose significant health risks. Chelation therapy, for example, involves using medications to remove heavy metals from the body, but it can cause serious side effects, such as kidney damage and seizures. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, but it has not been shown to be effective for autism and may cause lung damage. Before considering any therapy for autism, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional and to carefully evaluate the scientific evidence supporting its use. Relying on anecdotal evidence or testimonials can be misleading and potentially harmful. The promotion of unproven therapies contributes significantly to the autism controversy and can exploit vulnerable families seeking help for their children.
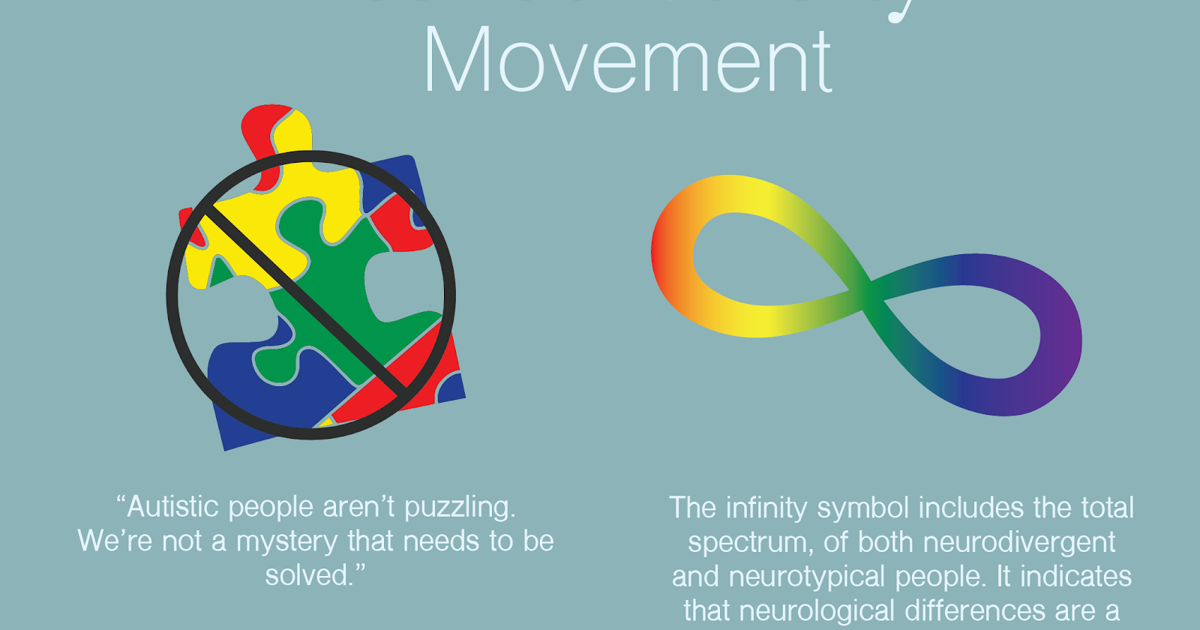
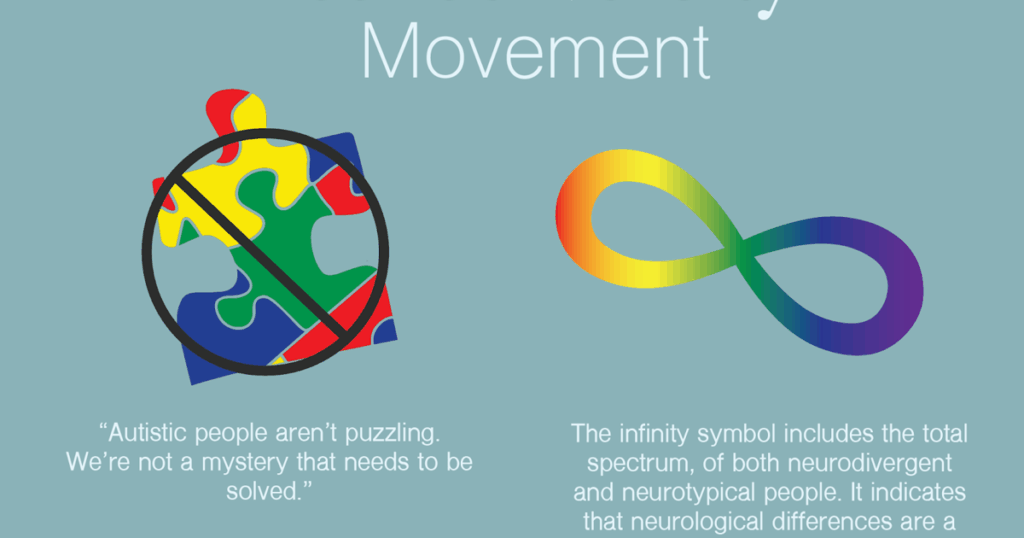
The Neurodiversity Movement: Celebrating Differences vs. Minimizing Challenges
The neurodiversity movement advocates for accepting and celebrating neurological differences, including autism, as natural variations of the human brain. Proponents of neurodiversity argue that autism should not be viewed as a disorder to be cured but rather as a different way of experiencing the world. This perspective has gained increasing traction in recent years, leading to a shift in attitudes toward autism and a greater emphasis on inclusion and acceptance.
The Strengths-Based Approach: Focusing on Abilities
The neurodiversity movement encourages a strengths-based approach to autism, focusing on the unique abilities and talents that individuals with autism may possess. Many people with autism have exceptional skills in areas such as mathematics, science, and art. By recognizing and nurturing these strengths, individuals with autism can thrive and contribute to society in meaningful ways. This approach also emphasizes the importance of creating supportive environments that accommodate the sensory sensitivities and communication styles of individuals with autism. [See also: The Neurodiversity Paradigm]
Potential Criticisms: Addressing the Needs of All Individuals
While the neurodiversity movement has been instrumental in promoting acceptance and understanding of autism, it has also faced criticism. Some argue that it minimizes the challenges and difficulties that many individuals with autism experience, particularly those with significant cognitive or behavioral impairments. They contend that focusing solely on strengths can neglect the need for interventions and supports to address these challenges. Finding a balance between celebrating neurodiversity and providing appropriate supports is crucial for ensuring that all individuals with autism have the opportunity to reach their full potential. This balance is at the heart of a crucial debate within the autism controversy.
Diagnostic Criteria: Broadening the Spectrum and Its Implications
The diagnostic criteria for autism have evolved over time, leading to a broadening of the autism spectrum. The current diagnostic criteria, outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), encompass a wide range of symptoms and severity levels. This broadening of the spectrum has led to an increase in autism diagnoses, raising questions about whether some individuals who are now diagnosed with autism would have been diagnosed with something else or not at all in the past.
Potential Benefits: Increased Awareness and Access to Services
The broadening of the autism spectrum has several potential benefits. It has increased awareness of autism and led to greater access to services and supports for individuals who might have previously been overlooked. It has also facilitated earlier diagnosis, which can lead to earlier intervention and improved outcomes. Furthermore, it has helped to destigmatize autism and promote greater acceptance of neurodiversity.
Potential Concerns: Overdiagnosis and Resource Allocation
However, the broadening of the autism spectrum also raises concerns about overdiagnosis and the potential for misdiagnosis. Some worry that individuals with other conditions, such as social anxiety or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), may be incorrectly diagnosed with autism. Overdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary interventions and stigmatization. Additionally, the increasing number of autism diagnoses can strain resources and make it more difficult for individuals with significant needs to access the services they require. Careful and accurate diagnosis is essential to ensure that individuals receive the appropriate care and support. This aspect of diagnostic accuracy is a critical element of the autism controversy.
The Role of Media and Public Perception
The media plays a significant role in shaping public perception of autism. Accurate and responsible reporting can help to promote understanding and acceptance, while sensationalized or misleading stories can perpetuate stereotypes and misinformation. It is essential for journalists and other media professionals to consult with experts and to avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes. Personal stories, while valuable, should be presented in a balanced and nuanced way, avoiding generalizations about the autism experience. Social media also plays a complex role, providing a platform for individuals with autism to share their experiences and connect with others, but also contributing to the spread of misinformation and the formation of echo chambers.
Moving Forward: Promoting Understanding and Collaboration
Navigating the autism controversy requires a commitment to evidence-based practices, ethical considerations, and respectful dialogue. It is essential to prioritize the needs and well-being of individuals with autism and their families, while also acknowledging the diverse perspectives and experiences within the autism community. Promoting collaboration between researchers, clinicians, educators, and individuals with autism is crucial for advancing our understanding of autism and developing effective interventions. By fostering open communication and embracing a spirit of inquiry, we can move beyond the autism controversy and create a more inclusive and supportive society for all.
Ultimately, the autism controversy highlights the need for continued research, critical thinking, and compassionate understanding. By engaging in informed discussions and challenging misinformation, we can work towards a future where individuals with autism are valued, respected, and empowered to reach their full potential.