Beta Glucan: Unlocking the Power of Nature’s Immune Booster
In the ever-evolving landscape of health and wellness, individuals are increasingly seeking natural solutions to bolster their immune systems and overall well-being. One such solution gaining significant traction is beta glucan. This naturally occurring polysaccharide, found in various sources like yeast, oats, and mushrooms, has been the subject of extensive research, revealing its potential to enhance immune function and offer a range of other health benefits. This article delves into the world of beta glucan, exploring its sources, mechanisms of action, proven benefits, and considerations for use.
What is Beta Glucan?
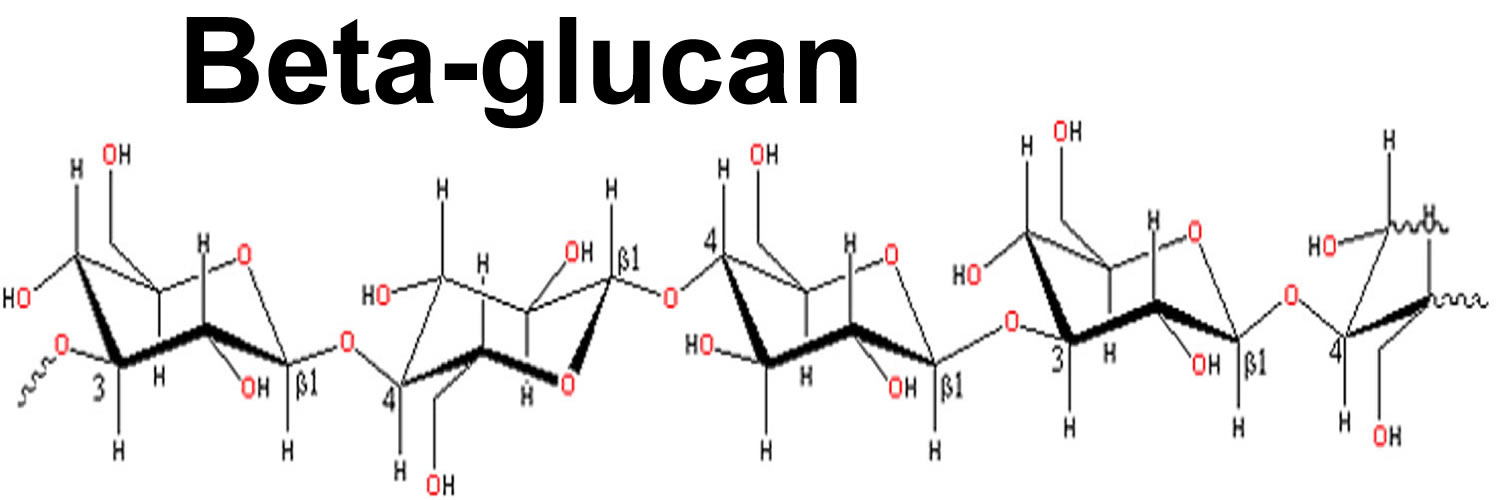
Beta glucans are a group of polysaccharides, specifically complex carbohydrates, found in the cell walls of bacteria, fungi, yeast, algae, and plants like oats and barley. They are classified based on their molecular structure, specifically the type of glycosidic bonds that link glucose molecules together. The most common types of beta glucans are beta-1,3-glucan, beta-1,4-glucan, and beta-1,6-glucan. These structural differences influence their biological activity and solubility.
The term “beta glucan” is a broad one encompassing a diverse family of molecules. The source of the beta glucan significantly impacts its properties and efficacy. For example, beta glucans derived from yeast and mushrooms tend to have stronger immunostimulatory effects compared to those from grains like oats.
Sources of Beta Glucan
Beta glucans can be sourced from a variety of natural sources, each offering a unique profile of beta glucan types and concentrations. Understanding these sources is crucial for selecting the right beta glucan supplement or incorporating beta glucan-rich foods into your diet.
- Yeast: Baker’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is a common source of beta-1,3/1,6-glucan. These yeast-derived beta glucans are well-researched and known for their potent immune-enhancing properties.
- Mushrooms: Certain medicinal mushrooms, such as shiitake, maitake, reishi, and turkey tail, are rich in beta glucans, particularly beta-1,3/1,6-glucans. These mushroom beta glucans have been used in traditional medicine for centuries to support immune health and overall well-being.
- Oats and Barley: These grains contain beta-1,3/1,4-glucan, which is primarily known for its cholesterol-lowering effects and gut health benefits.
- Algae: Some species of algae also contain beta glucans, offering a potential alternative source.
How Beta Glucan Works: Mechanisms of Action
The primary mechanism by which beta glucans exert their beneficial effects is through their interaction with the immune system. Specifically, beta glucans bind to receptors on immune cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, and natural killer (NK) cells. This binding activates these immune cells, priming them to respond more effectively to threats like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. [See also: Gut Health and Immunity]
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
- Binding to Immune Cells: Beta glucans bind to receptors like Dectin-1 on immune cells.
- Immune Cell Activation: This binding triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling pathways, leading to activation of the immune cell.
- Enhanced Immune Response: Activated immune cells exhibit increased phagocytosis (engulfing and destroying pathogens), enhanced production of cytokines (signaling molecules that coordinate immune responses), and improved cytotoxic activity (killing infected or cancerous cells).
Beyond their direct effects on immune cells, beta glucans can also indirectly modulate the immune system by influencing the gut microbiome. They can act as prebiotics, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which further supports immune health.
Proven Benefits of Beta Glucan
Numerous studies have investigated the potential health benefits of beta glucan. While research is ongoing, the existing evidence suggests that beta glucan may offer the following advantages:
- Immune Support: This is the most well-established benefit. Beta glucans have been shown to enhance immune function, reduce the incidence and severity of upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) like colds and flu, and improve the response to vaccines.
- Cholesterol Reduction: Beta glucans from oats and barley are known to lower LDL cholesterol levels, contributing to heart health. They achieve this by binding to bile acids in the gut, preventing their reabsorption and promoting cholesterol excretion.
- Blood Sugar Control: Some studies suggest that beta glucans may help improve blood sugar control, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes. They can slow down the absorption of glucose from the gut, preventing blood sugar spikes.
- Gut Health: Beta glucans can act as prebiotics, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a healthy gut microbiome. This can improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and further support immune function.
- Anti-Cancer Potential: Research suggests that beta glucans may have anti-cancer properties. They can enhance the activity of NK cells, which play a crucial role in killing cancer cells. Additionally, they may help modulate the immune response to cancer, making it more effective. [See also: Natural Cancer Therapies]
- Wound Healing: Some studies indicate that beta glucans may promote wound healing by stimulating collagen synthesis and reducing inflammation.
Beta Glucan Supplements: What to Consider
Beta glucan supplements are widely available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. When choosing a beta glucan supplement, consider the following factors:
- Source: Opt for supplements derived from well-researched sources like yeast or medicinal mushrooms.
- Beta Glucan Type: Look for supplements that specify the type of beta glucan (e.g., beta-1,3/1,6-glucan). This information can help you understand the potential benefits and efficacy of the product.
- Purity and Potency: Choose supplements from reputable manufacturers that provide information on the purity and potency of their products.
- Dosage: Follow the recommended dosage instructions on the product label or consult with a healthcare professional.
- Third-Party Testing: Look for supplements that have been tested by a third-party organization for quality and purity.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Beta glucan is generally considered safe for most people. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as gas, bloating, or diarrhea, especially when taking high doses. It is always recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase it as tolerated. [See also: Managing Digestive Issues]
While generally safe, it is important to be aware of potential interactions. Beta glucans may interact with immunosuppressant medications. If you are taking any medications or have any underlying health conditions, consult with a healthcare professional before taking beta glucan supplements.
The Future of Beta Glucan Research
Research on beta glucan is ongoing, and future studies are likely to further elucidate its potential health benefits and mechanisms of action. Areas of particular interest include:
- Cancer Therapy: Investigating the role of beta glucans in enhancing the efficacy of cancer treatments and preventing cancer recurrence.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Exploring the potential of beta glucans to modulate the immune system in autoimmune diseases.
- Vaccine Adjuvant: Evaluating the use of beta glucans as vaccine adjuvants to enhance the immune response to vaccines.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Beta Glucan
Beta glucan represents a promising natural compound with the potential to enhance immune function, support heart health, improve blood sugar control, and offer a range of other health benefits. By understanding its sources, mechanisms of action, and potential benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating beta glucan into their health and wellness routines. Whether through beta glucan-rich foods or supplements, harnessing the power of this natural immune booster can contribute to a healthier and more resilient life. As with any supplement, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial, especially for those with existing health conditions or those taking medications. The future of beta glucan research holds great promise, and ongoing studies are likely to uncover even more of its potential benefits for human health.