Navigating the Fury: Understanding Weather Storms and Tornadoes
Weather storms and tornadoes represent some of nature’s most destructive forces. From torrential rain and powerful winds to the intense vortexes of tornadoes, these phenomena pose significant threats to life and property. Understanding the science behind these weather events, recognizing warning signs, and knowing how to prepare are crucial for mitigating their impact. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of weather storms and tornadoes, covering their formation, characteristics, and safety measures.
The Anatomy of Weather Storms
Weather storms encompass a wide range of atmospheric disturbances, each with its own unique characteristics. Common types include thunderstorms, hurricanes, blizzards, and heat waves. These storms are driven by various factors, including temperature gradients, atmospheric pressure differences, and moisture availability.
Thunderstorms: A Symphony of Lightning and Thunder
Thunderstorms are perhaps the most common type of weather storm. They develop when warm, moist air rises rapidly into the atmosphere, creating towering cumulonimbus clouds. These clouds contain ice crystals and water droplets, which collide and generate electrical charges. When the electrical potential becomes strong enough, lightning strikes occur, followed by the sound of thunder. Thunderstorms can also produce heavy rain, strong winds, and hail. [See also: Lightning Safety Tips]
Hurricanes: The Cyclonic Giants
Hurricanes, also known as typhoons or cyclones depending on their location, are massive rotating storms that form over warm ocean waters. They are characterized by sustained winds of at least 74 miles per hour and a distinct eye at their center. Hurricanes draw energy from the warm ocean, and their intensity can increase rapidly as they move over water. They bring with them devastating winds, torrential rain, and storm surges that can inundate coastal areas. The impact of a weather storm like a hurricane can be felt for hundreds of miles.
Blizzards: Whiteouts and Frigid Temperatures
Blizzards are severe winter storms characterized by heavy snowfall, strong winds, and low temperatures. The combination of these factors can create whiteout conditions, making it difficult to see and navigate. Blizzards can also lead to power outages, transportation disruptions, and hypothermia. Preparing for a blizzard involves stocking up on food, water, and supplies, and ensuring that your home is adequately insulated.
Heat Waves: Silent Killers
Heat waves are prolonged periods of abnormally hot weather. They can pose a significant health risk, especially to vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. Heat waves can lead to heatstroke, dehydration, and other heat-related illnesses. Staying hydrated, seeking shade, and avoiding strenuous activity during the hottest part of the day are crucial for protecting yourself during a heat wave. The dangers of a weather storm like a heatwave are often underestimated.
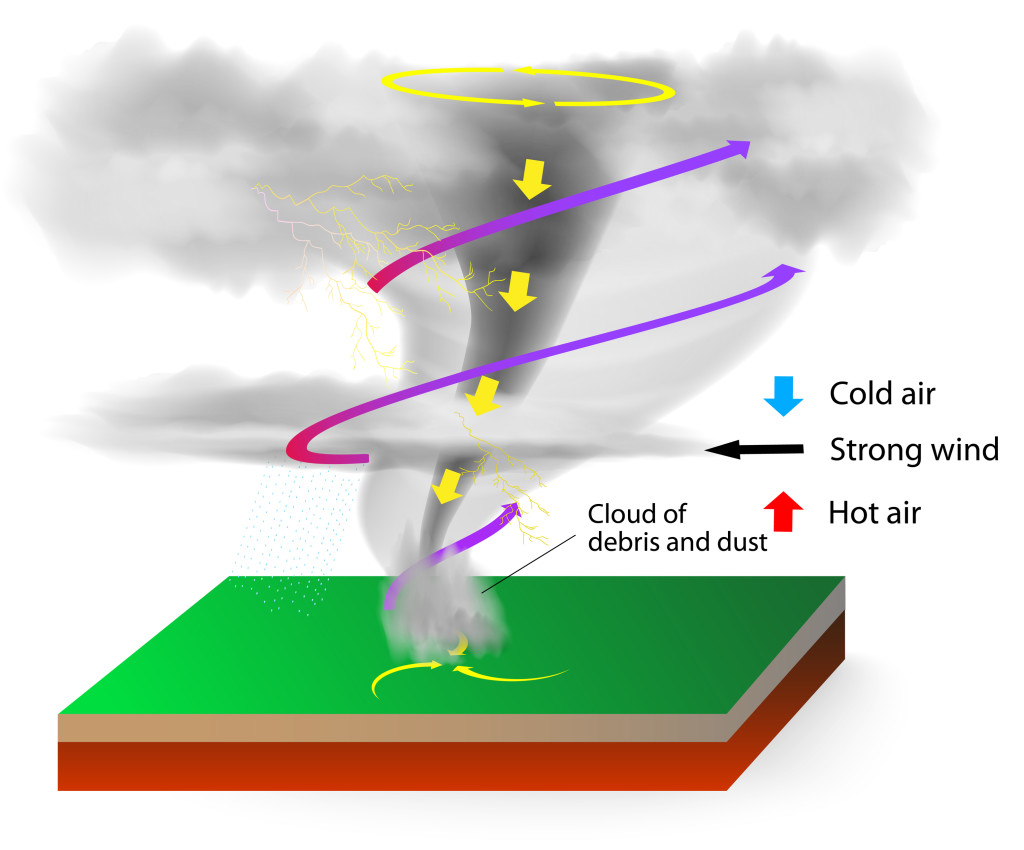
Tornadoes: Nature’s Violent Whirlwinds
Tornadoes are violently rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground. They are among the most destructive weather phenomena, capable of producing winds exceeding 300 miles per hour. Tornadoes can cause widespread damage, uprooting trees, destroying buildings, and even lifting cars into the air. Understanding how tornadoes form and recognizing the warning signs are essential for staying safe. The sheer power of a weather storm as a tornado is awe-inspiring and frightening.
Formation of Tornadoes
Tornadoes typically form within severe thunderstorms known as supercells. Supercells are characterized by rotating updrafts called mesocyclones. When a mesocyclone descends to the ground and interacts with the surface, it can trigger the formation of a tornado. The exact mechanisms that lead to tornado formation are still not fully understood, but atmospheric instability, wind shear, and moisture availability are all important factors.
The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale
The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale is used to rate the intensity of tornadoes based on the damage they cause. The scale ranges from EF0 to EF5, with EF0 tornadoes causing minor damage and EF5 tornadoes causing catastrophic damage. The EF scale takes into account various factors, including the type of structure damaged, the degree of damage, and the quality of construction. Understanding the EF scale can help you assess the potential threat posed by a tornado. The scale helps quantify the impact of a weather storm manifested as a tornado.
Recognizing Tornado Warning Signs
Being able to recognize the warning signs of a tornado can save your life. These signs include a dark, greenish sky, large hail, a loud roar or rumble, and a rotating cloud base. If you see any of these signs, seek shelter immediately. The earlier you recognize the signs of a potential weather storm that could lead to a tornado, the better.
Preparing for Weather Storms and Tornadoes
Preparation is key to mitigating the impact of weather storms and tornadoes. This involves developing a plan, assembling a disaster kit, and staying informed about weather conditions. [See also: Emergency Preparedness Checklist]
Developing a Disaster Plan
Your disaster plan should outline what to do in the event of a weather storm or tornado. This includes identifying safe places to take shelter, establishing communication protocols, and practicing evacuation routes. Make sure everyone in your household is familiar with the plan. A well-thought-out plan is crucial when facing a weather storm.
Assembling a Disaster Kit
Your disaster kit should contain essential supplies such as food, water, medicine, a first-aid kit, a flashlight, a battery-powered radio, and extra batteries. It’s also a good idea to include personal items such as important documents, cash, and a change of clothes. Regularly check and replenish your kit to ensure that the supplies are fresh and in good condition. Having a disaster kit prepared is essential for any weather storm.
Staying Informed
Stay informed about weather conditions by monitoring local news, weather websites, and social media. Pay attention to weather alerts and warnings issued by the National Weather Service. Having a NOAA weather radio can be invaluable during a power outage. Being informed is the first step to protecting yourself from a weather storm. Knowing the potential risks from weather storms is a necessity in today’s world.
Safety Measures During Weather Storms and Tornadoes
Knowing what to do during a weather storm or tornado can significantly increase your chances of survival. The specific safety measures will vary depending on the type of storm, but some general guidelines apply.
During a Thunderstorm
Seek shelter indoors and avoid contact with electrical appliances and plumbing. Stay away from windows and doors. If you are outdoors, find a low-lying area away from trees and power lines. Remember, when thunder roars, go indoors! The dangers of a weather storm like a thunderstorm should not be underestimated.
During a Hurricane
Evacuate if instructed to do so by local authorities. If you are unable to evacuate, seek shelter in a sturdy, interior room on the lowest level of your home. Stay away from windows and doors. Have your disaster kit readily available. The intensity of a weather storm like a hurricane demands respect and careful planning.
During a Blizzard
Stay indoors and avoid unnecessary travel. If you must go outside, dress in layers and cover exposed skin. Be aware of the signs of hypothermia and frostbite. If you are stranded in your car, stay inside and wait for help to arrive. The cold and isolation of a weather storm like a blizzard can be deadly.
During a Heat Wave
Stay indoors in an air-conditioned environment. Drink plenty of fluids and avoid strenuous activity. Wear light-colored, loose-fitting clothing. Check on elderly neighbors and relatives. The insidious nature of a weather storm like a heatwave requires vigilance.
During a Tornado
Seek shelter in a basement, storm cellar, or interior room on the lowest level of your home. If you are in a car or mobile home, abandon it and find a sturdy building. Cover your head and neck with your arms. The unpredictability of a weather storm like a tornado makes preparedness paramount. The devastation caused by a weather storm such as a tornado can be immense, emphasizing the need for safety precautions.
The Role of Technology in Weather Forecasting
Advancements in technology have significantly improved our ability to forecast weather storms and tornadoes. Doppler radar, satellite imagery, and computer models provide valuable data that meteorologists use to predict the intensity and path of these events. Early warning systems allow communities to prepare and evacuate in advance, saving lives. The impact of weather storms can be mitigated by using available technology to predict and prepare.
Conclusion
Weather storms and tornadoes are powerful forces of nature that can have devastating consequences. By understanding the science behind these events, recognizing warning signs, and taking appropriate safety measures, we can significantly reduce their impact. Staying informed, being prepared, and acting responsibly are key to navigating the fury of weather storms and tornadoes. Remember, knowledge is power, and preparedness is the best defense against these natural hazards. The importance of understanding and preparing for weather storms cannot be overstated. Even with advanced technology, nature’s power, especially during a weather storm, demands respect and caution.
