Fluoride and Pineal Gland Calcification: Unveiling the Truth
The purported link between fluoride exposure and pineal gland calcification has been a subject of ongoing debate and research. This article aims to provide a balanced and informative overview of the current understanding of this complex issue, exploring the science, the concerns, and the available evidence.
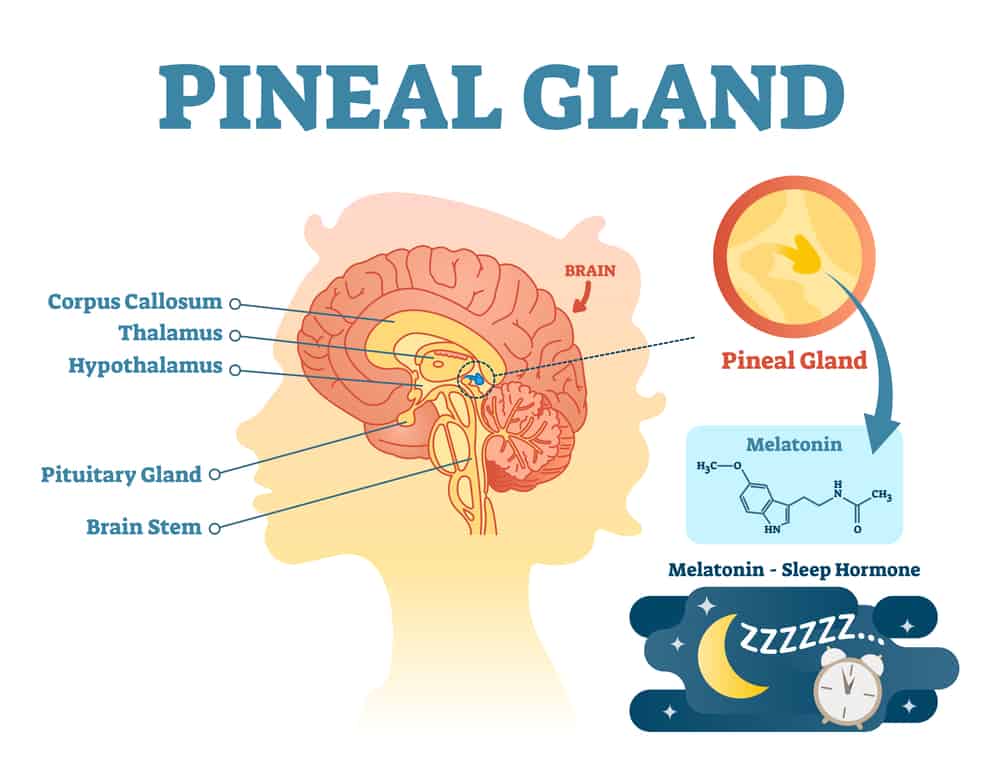
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that is widely added to public water supplies and dental products to prevent tooth decay. While its benefits for dental health are well-established, concerns have been raised about its potential adverse effects on other parts of the body, particularly the pineal gland. This small, cone-shaped gland located in the brain plays a crucial role in regulating sleep cycles and hormone production, primarily melatonin.
Understanding Pineal Gland Calcification
Pineal gland calcification, also known as fluoride accumulation in the pineal gland, is a natural process that occurs with age. It involves the deposition of calcium phosphate crystals within the gland’s tissue. Several factors can contribute to this calcification, including aging, exposure to certain toxins, and, according to some research, fluoride exposure.
The pineal gland is unique in that it lacks the blood-brain barrier, making it more susceptible to accumulating substances from the bloodstream, including fluoride. Studies have shown that fluoride can accumulate in the pineal gland at higher concentrations than in other tissues.
The Fluoride-Pineal Gland Connection: What the Research Says
The potential link between fluoride and pineal gland calcification has been investigated in several studies. A notable study published in *Caries Research* in 2001, found that fluoride accumulated in the pineal glands of deceased individuals. The study also suggested a possible correlation between fluoride levels in the pineal gland and decreased melatonin production. However, it is important to note that this study was conducted on deceased individuals, and further research is needed to confirm these findings in living subjects.
Another study published in *Neurotoxicology and Teratology* examined the effects of fluoride on the pineal gland of rats. The results indicated that high doses of fluoride could lead to structural and functional changes in the pineal gland, including decreased melatonin synthesis. Again, the dosage used in the rat study was significantly higher than what is typically encountered through fluoridated water, and extrapolation to humans needs to be done with caution. [See also: Water Fluoridation and Public Health]
While some studies suggest a potential link, other research has yielded conflicting results. A review published in the *Journal of the American Dental Association* concluded that the available evidence is insufficient to establish a causal relationship between fluoride exposure and adverse effects on the pineal gland. The review highlighted the limitations of existing studies, such as small sample sizes, methodological inconsistencies, and the lack of long-term data.
Potential Health Implications of Pineal Gland Calcification
If fluoride induced pineal gland calcification affects melatonin production, it could theoretically lead to a range of health issues. Melatonin plays a vital role in regulating sleep-wake cycles, immune function, and antioxidant defense. Reduced melatonin levels have been linked to sleep disorders, mood disturbances, and an increased risk of certain diseases. [See also: The Importance of Melatonin for Sleep]
Some proponents of fluoride-free water argue that pineal gland calcification caused by fluoride exposure could contribute to these health problems. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that the scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited and inconclusive. More research is needed to determine the extent to which fluoride affects pineal gland function and whether this has any significant health consequences.
Addressing the Concerns: Mitigation Strategies
For individuals concerned about the potential effects of fluoride on the pineal gland, several strategies can be considered:
- Reduce Fluoride Intake: This can be achieved by using fluoride-free toothpaste, avoiding fluoridated water (using a water filter that removes fluoride), and limiting consumption of processed foods and beverages that may contain fluoride.
- Increase Melatonin Production: Natural ways to boost melatonin levels include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a dark and quiet sleep environment, and exposing yourself to sunlight during the day.
- Consume Foods Rich in Magnesium: Magnesium is essential for various bodily functions, including pineal gland health. Magnesium-rich foods include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Consider Supplements: Some supplements, such as iodine and boron, are believed to help remove fluoride from the body. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
The Ongoing Debate and Future Research
The debate surrounding fluoride and pineal gland calcification is likely to continue. While some studies suggest a potential link, the evidence remains inconclusive. More rigorous research is needed to determine the long-term effects of fluoride exposure on the pineal gland and its impact on overall health.
Future research should focus on:
- Longitudinal studies that track the effects of fluoride exposure on pineal gland function and melatonin production over time.
- Studies that examine the effects of different fluoride doses on the pineal gland.
- Research on the mechanisms by which fluoride may affect the pineal gland.
In conclusion, the relationship between fluoride and pineal gland calcification is a complex and controversial topic. While some studies suggest a potential link, the evidence is not conclusive. Individuals concerned about this issue can take steps to reduce their fluoride intake and support pineal gland health through dietary and lifestyle modifications. Continued research is essential to fully understand the potential effects of fluoride on the pineal gland and overall health.
It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals and dental experts to make informed decisions about fluoride exposure and oral health.
