What Causes White Mucus in Stool: Understanding the Reasons and When to Seek Help
Finding white mucus in stool can be alarming, prompting immediate concerns about your digestive health. While occasional mucus is normal, persistent or excessive amounts, especially white mucus in stool, warrant investigation. This article delves into the common causes of white mucus in stool, offering insights into when medical attention is necessary and providing a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
Understanding Mucus and Its Role in the Digestive System
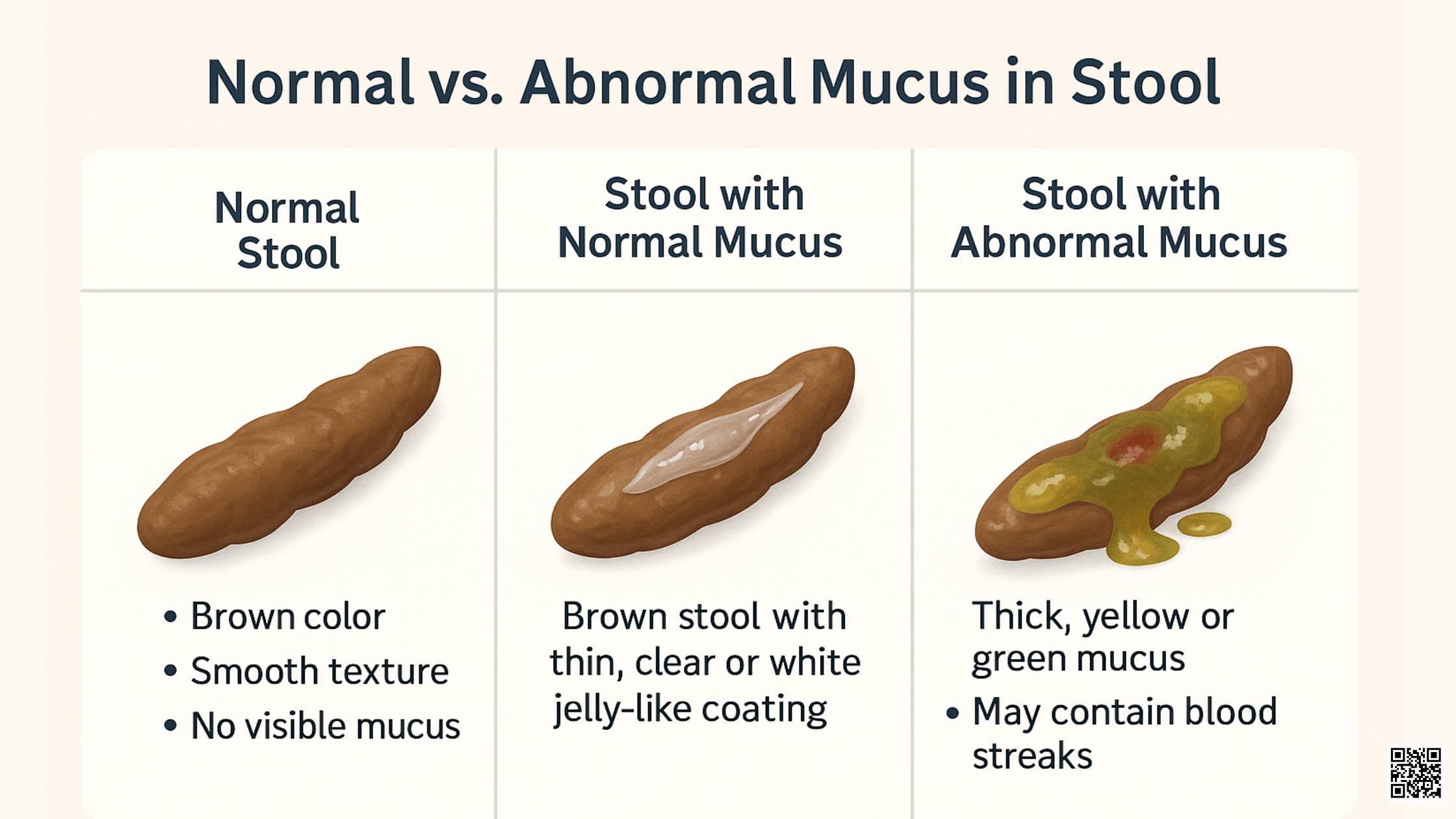
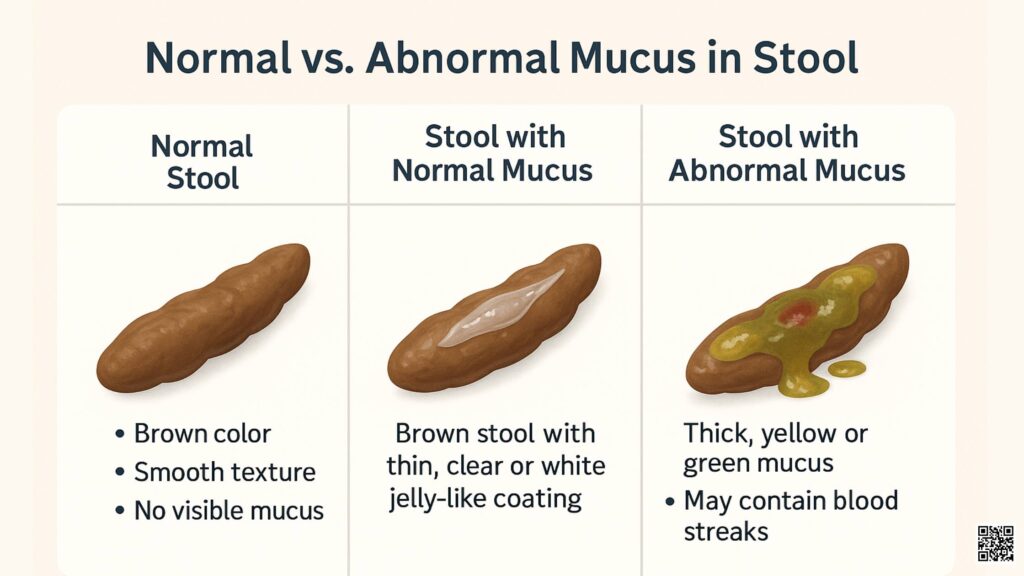
Mucus is a jelly-like substance produced throughout the body, including the digestive tract. Its primary function is to lubricate and protect the lining of the intestines, facilitating the smooth passage of stool. Small amounts of mucus are naturally present in feces and are usually unnoticeable. However, certain conditions can lead to an increase in mucus production, resulting in visible white mucus in stool.
Common Causes of White Mucus in Stool
Several factors can contribute to the presence of white mucus in stool. It’s crucial to identify the underlying cause to determine the appropriate course of action. Here are some of the most common reasons:
Infections
Infections, whether bacterial, viral, or parasitic, can irritate the intestinal lining and trigger increased mucus production. Common culprits include:
- Bacterial Infections: Infections like Salmonella or Campylobacter can cause inflammation and diarrhea, often accompanied by white mucus in stool.
- Viral Infections: Viruses like norovirus or rotavirus can also lead to gastroenteritis, resulting in increased mucus production.
- Parasitic Infections: Parasites such as Giardia can infect the intestines, causing inflammation and the presence of white mucus in stool.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
IBD encompasses chronic inflammatory conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions cause persistent inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to various symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and white mucus in stool. The inflammation damages the intestinal lining, prompting the body to produce more mucus as a protective response. [See also: Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease Symptoms]
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a common disorder that affects the large intestine. While it doesn’t cause inflammation like IBD, it can disrupt bowel function and lead to changes in stool consistency, including the presence of white mucus in stool. IBS is often triggered by stress, diet, or changes in gut bacteria. [See also: Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Through Diet]
Food Intolerances and Allergies
Food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity, can irritate the digestive system and cause increased mucus production. Allergic reactions to certain foods can also trigger inflammation and the appearance of white mucus in stool. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods can often alleviate these symptoms.
Constipation
Ironically, constipation can also lead to the presence of white mucus in stool. When stool remains in the colon for an extended period, it can become dry and hard. The body may produce extra mucus to lubricate the stool and facilitate its passage. This is often accompanied by straining during bowel movements.
Anal Fissures and Hemorrhoids
Anal fissures (small tears in the lining of the anus) and hemorrhoids (swollen veins in the rectum and anus) can cause irritation and inflammation, leading to the production of mucus. While these conditions primarily cause bleeding, mucus may also be present in the stool.
Dietary Factors
Certain dietary factors can contribute to increased mucus production. For example, a diet high in fiber can sometimes lead to more mucus in the stool as the body works to process the increased bulk. Dehydration can also exacerbate the problem, as it can lead to harder stools that require more lubrication. [See also: The Role of Fiber in Digestive Health]
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional white mucus in stool may not be a cause for concern, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent mucus in stool: If you consistently notice white mucus in stool for more than a few days, it’s crucial to consult a doctor.
- Blood in stool: The presence of blood, whether bright red or dark and tarry, is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention.
- Abdominal pain: Severe or persistent abdominal pain, especially when accompanied by white mucus in stool, could indicate a more serious underlying condition.
- Changes in bowel habits: Significant changes in bowel habits, such as persistent diarrhea or constipation, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, and should be discussed with a doctor.
- Fever: A fever accompanied by gastrointestinal symptoms may indicate an infection that requires treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
To determine the cause of white mucus in stool, your doctor may recommend several diagnostic tests, including:
- Stool Sample: A stool sample can help identify infections, parasites, or inflammatory markers.
- Colonoscopy: A colonoscopy involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the colon to visualize the lining and identify any abnormalities.
- Sigmoidoscopy: Similar to a colonoscopy, but it only examines the lower portion of the colon.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help detect inflammation or other markers of disease.
- Food Allergy Testing: If food allergies are suspected, allergy testing can help identify trigger foods.
Treatment for white mucus in stool depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
- Antiviral Medications: For viral infections (though often, treatment is supportive).
- Anti-parasitic Medications: For parasitic infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: For IBD, to reduce inflammation.
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding trigger foods for food intolerances or allergies.
- Fiber Supplements: To regulate bowel movements in cases of constipation or IBS.
- Probiotics: To restore healthy gut bacteria.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing stress and staying hydrated.
Preventing White Mucus in Stool
While not all causes of white mucus in stool are preventable, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently to prevent infections.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Identify and Avoid Trigger Foods: If you suspect a food intolerance or allergy, work with a healthcare professional to identify and avoid trigger foods.
Conclusion
The presence of white mucus in stool can be a sign of various underlying conditions, ranging from minor irritations to more serious diseases. While occasional mucus is usually harmless, persistent or excessive amounts warrant medical evaluation. By understanding the potential causes and knowing when to seek help, you can take proactive steps to protect your digestive health. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing underlying conditions and preventing complications. If you are concerned about white mucus in stool, consult with your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. They can properly assess your symptoms and help you regain control over your digestive health and overall well-being.